ISO 14001 is an internationally recognized standard for Environmental Management Systems (EMS), providing a framework for organizations to protect the environment, respond to changing environmental conditions, and enhance environmental performance. Whether you’re a business owner, environmental manager, or a sustainability enthusiast, understanding ISO 14001 can significantly benefit your organization and the environment. Here are ten crucial things you should know about ISO 14001.
- 1. What is ISO 14001?
- 2. Core Elements of ISO 14001
- 3.Benefits of ISO 14001 Certification
- 4.ISO 14001 and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
- 5. Risk-Based Thinking
- 6. Life Cycle Perspective
- 7. Integration with Other Management Systems
- 8. Employee Involvement
- 9. Continuous Improvement
- 10. Global Relevance and Recognition
- How to get Iso 9001?
- Conclusion
1. What is ISO 14001?
ISO 14001 is part of the ISO 14000 family of standards, which are designed to help organizations minimize their environmental impact. It provides a systematic approach to managing environmental responsibilities and enhancing overall environmental performance.
Example: A manufacturing company can use ISO 14001 to reduce waste, improve resource efficiency, and decrease its carbon footprint.
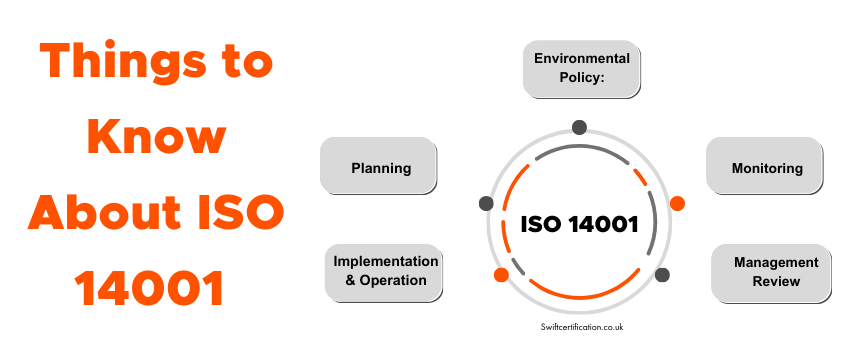
2. Core Elements of ISO 14001
The standard is built around several core elements that guide organizations in their environmental management efforts:
- Environmental Policy: Commitment to environmental protection and continual improvement.
- Planning: Identifying environmental aspects, legal requirements, and objectives.
- Implementation and Operation: Defining roles, training, and operational controls.
- Checking and Corrective Action: Monitoring, measuring, and correcting deviations.
- Management Review: Periodic review of the EMS by top management.
Example: A retail chain can implement these elements to ensure all stores comply with environmental regulations and company policies.
3.Benefits of ISO 14001 Certification
ISO 14001 certification offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Environmental Performance: Systematic approach to managing environmental impacts.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring adherence to environmental laws and regulations.
- Cost Savings: Reducing waste and energy consumption can lead to significant cost savings.
- Enhanced Reputation: Demonstrating a commitment to environmental responsibility can enhance brand image and customer trust.
Example: A construction company may gain a competitive edge by showcasing its ISO 14001 certification in bids and proposals.
4.ISO 14001 and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Adopting ISO 14001 is a strong indicator of an organization’s commitment to CSR. It aligns with broader CSR goals, such as sustainable development, ethical business practices, and social accountability.
Example: A tech company might use its ISO 14001 certification as part of its CSR strategy to attract socially conscious investors and customers.
5. Risk-Based Thinking
ISO 14001 emphasizes risk-based thinking, requiring organizations to consider environmental risks and opportunities in their planning processes. This proactive approach helps in identifying potential environmental impacts and mitigating them before they occur.
Example: A food processing company could identify the risk of water pollution from its operations and implement measures to prevent contamination.
6. Life Cycle Perspective
The standard encourages organizations to consider the entire life cycle of their products or services, from raw material extraction to disposal. This holistic view helps in identifying environmental impacts at each stage and finding ways to mitigate them.
Example: A clothing manufacturer might assess the environmental impact of fabric production, dyeing, and disposal, and seek sustainable alternatives.
7. Integration with Other Management Systems
ISO 14001 can be easily integrated with other management systems, such as ISO 9001 (Quality Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety). This integration allows for a unified approach to managing various aspects of an organization’s operations.
Example: An automotive company might integrate ISO 14001 with ISO 9001 to simultaneously address quality and environmental concerns.
8. Employee Involvement
Engaging employees at all levels is crucial for the successful implementation of ISO 14001. Training and awareness programs help in building a culture of environmental responsibility within the organization.
Example: A hospital could conduct workshops and training sessions to educate staff about waste segregation and energy conservation.
9. Continuous Improvement
One of the key principles of ISO 14001 is the focus on continuous improvement. Organizations are encouraged to regularly review and enhance their EMS to achieve better environmental performance over time.
Example: A packaging company might continuously monitor its carbon emissions and set new targets for reduction each year.
10. Global Relevance and Recognition
ISO 14001 is globally recognized and applicable to any organization, regardless of size, type, or sector. Its widespread acceptance makes it a valuable certification for companies operating in international markets.
Example: A multinational corporation might adopt ISO 14001 across all its global facilities to ensure a consistent approach to environmental management.
How to get Iso 9001?
ISO Certification costs vary depending on your business, Swift Certification offer competitive pricing and a unique client led approach to our auditing services. Contact us today for a FREE, no obligation quote – Call us on 0161 470 5352 or fill out a form here and a member of our team will be in touch.
Conclusion
ISO 14001 is more than just a certification; it’s a commitment to sustainable environmental management and continuous improvement. By understanding and implementing the ten key aspects of ISO 14001, organizations can not only enhance their environmental performance but also reap significant economic and reputational benefits. Whether you’re looking to comply with regulations, reduce costs, or improve your corporate image, ISO 14001 provides a robust framework to achieve your environmental goals.
Learn more about Standards
ISO 9001 Quality
ISO 45001 Health & Safety
IS0 27001 Information Security
ISO 14001 Environmental



